编译器简介
简介 Introduction
-
编译器 Compilers
- 非实时 off-line
- 预处理 pre-process
-
解释器 Interpreters
- 实时 on-line
编译器的五个主要阶段
- Lexical Analysis 词法分析
- Parsing 解析
- Semantic Analysis 语义分析
- Optimization 优化
- Code Generation 代码生成
编译器结构 Structure of a Compiler
Lexical Analysis 词法分析
我们可以通过空格来区分单词
This is a Sentence
但如果是这样就很难区分了
ist his ase nte nce
词法分析将程序文本划分为“单词”或“标记”
if x == y the z = 1; else z = 2;
Parsing 解析
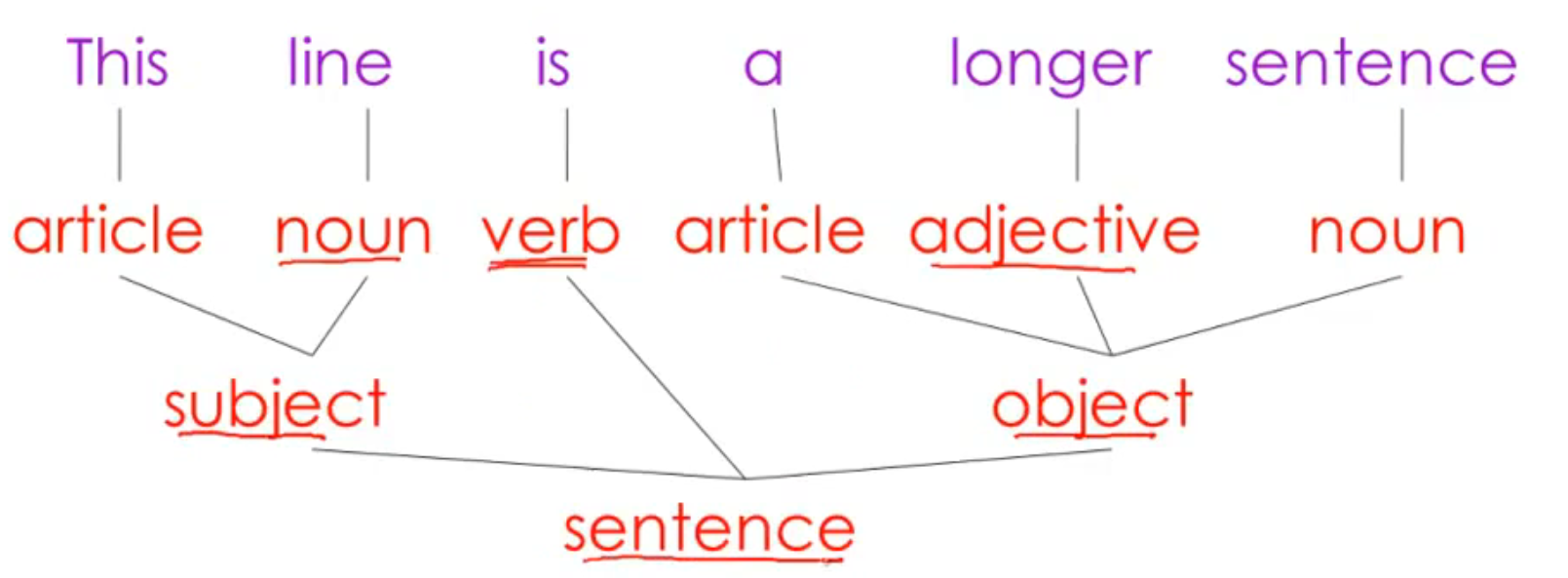
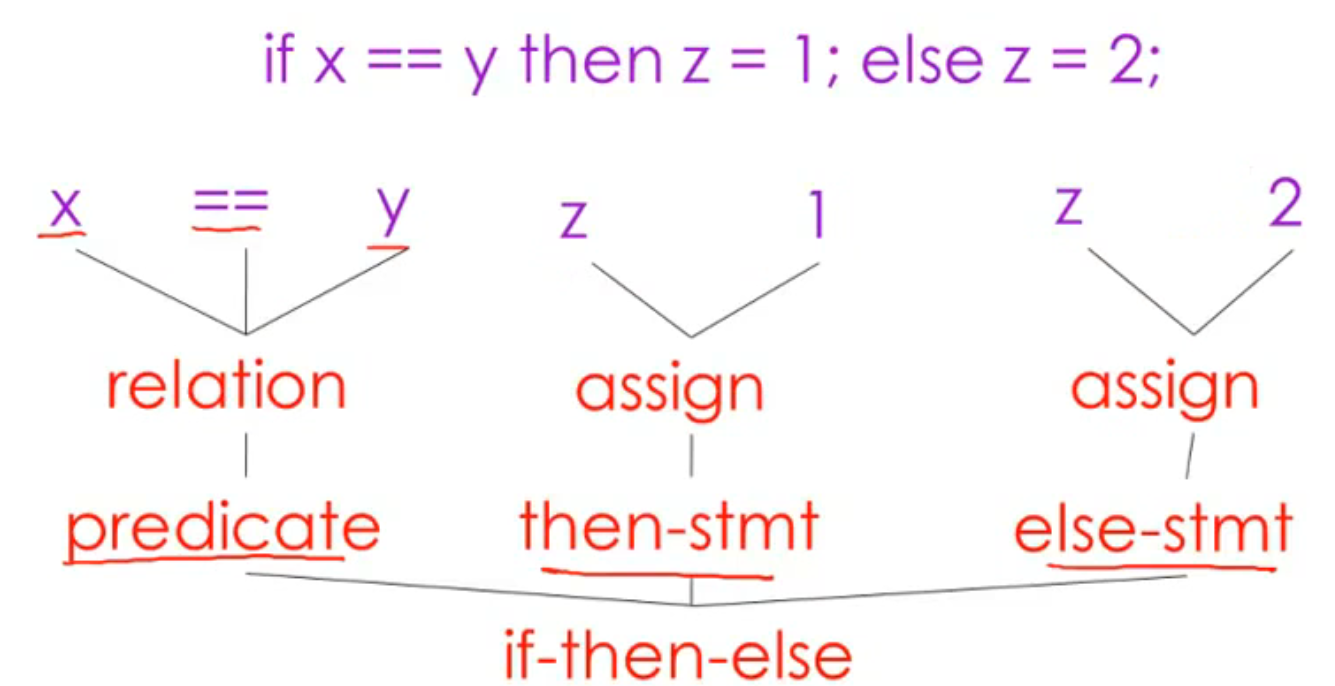
Semantic Analysis 语义分析
Jack said Jerry left his assignment at home.
我们明白其中his指的是Jack而不是Jerry
{
int Jack = 3;
{
int Jack = 4;
cout << Jack; // ?
}
}
其中输出的Jack也是块内的Jack
Optimization 优化
- 运行得更快 Run faster
- 更少的内存 Use less memory
- 减少资源 Reduce resources
E.G.
X = Y * 0 is the same as X = 0
当Y为整形时成立 valid for integers
当不Y为整形时不成立 invalid for FP
E.G. NAN * 0 = NAN
Code Generation 代码生成
-
生成汇编代码 Produces assembly code
-
翻译成其他语言 A translate into another language
现代编译器更注重优化
程序设计语言的经济性 The Economy of Programming Languages
Q: Why are there so many programming languages ?
Q: 为什么有这么多编程语言?
A: Application domains have distinctive/conflicting needs.
A: 应用程序领域具有不同/冲突的需求。
- 科学计算 scientific computing
- 良好的浮点 ( FP )
- 良好的阵列 ( arrays )
- 并行 ( parallelism )
E.G. FORTRAN
- 商务应用 business applications
- 持久 persistence
- 报告生成 report generation
- 数据分析 data analysis
E.G. SQL
- 系统编程 systems programming
- 资源控制 control of resources
- 实时约束real time constraints
E.G. C/C++
Q: Why are there new programming languages ?
Q: 为什么会有新的编程语言?
A: Programmer training is the dominant cost for a programming language.
A: 程序员培训是编程语言的主要成本。
- Widely used languages are slow to change
- 广泛使用的语言变化缓慢
- Easy to start a new language
- 轻松开始一门新语言
- Languages adapted to fill a void.
- 填补空白的语言
Q: What is a good programming language ?
Q: 什么是好的编程语言?
A: There is no universally accepted metric for language design.
A: 语言设计没有公认的度量标准。
License:
CC BY 4.0